Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
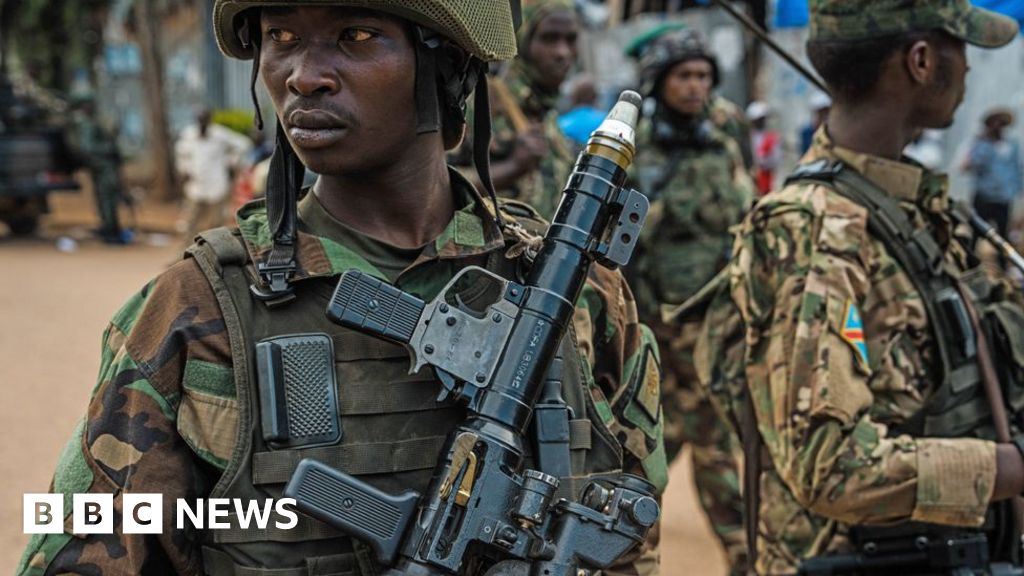

World Unit China, BBC World Service
 Gets the image
Gets the imageChina’s efforts to create huge business interests across Africa were accompanied by a careful maintenance policy of neutrality – but the conflict in the east of the Democratic Republic caused a shift in its approach.
Rwanda is widely accused of inciting fights in the region, rich minerals and Beijing, which has a close relationship with both Dr. Congo and Rwanda, has joined criticism in recent weeks.
But he is trying to go through a diplomatic sewer to maintain good relations with both countries, and continues to manage his business – and buy important minerals.
For decades, China has been careful not to take parties in Africa’s conflicts to avoid causing problems that may interfere with its broad commercial interests.
Until now, he has shy away from criticism of Africa’s governments for supporting conflict participants.
For example, China has said little about a series of courses since 2020 in the Sahel West African region, except to urge the leaders to consider people’s interests.
Beijing has long pursued a policy of not interfering in the internal affairs of another state, says prof. Zhou Yuian, who specializes in the development of African and security at the Shanghai Institute for International Studies (Siis).
Thus, this avoids the decision of the conflicts, except for a call to diplomatic or political efforts of international organizations such as the UN or the African Union.
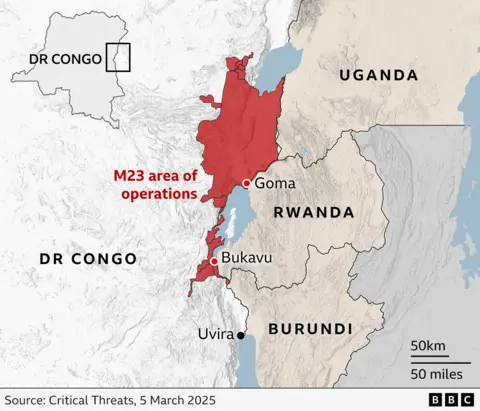
In 2021, in 2021, in 2021, there were riots related to the Rwandan M23 rebels in the east D -R Congo.
In its early comments on these events, China restricted criticism of unnamed “foreign forces” for supporting M23 fighters.
But in the last few weeks he broke from his usual practice and turned to Rwanda named.
This stems from the great income of M23, which since January has seized key cities of Homo and Bukov.
“China repeats the hope that Rwanda will cease its military support for M23 and immediately abandon all its military forces from the DRC,” the UN ambassador said in February.
Professor Zhou notes that, though significant, “the wording is generally relatively soft.”
“China” hoped that Rwanda would stop her support but did not condemn her, “he says.
However, China soon supported the UN Security Council resolution, which directly calls on Rwanda’s defense forces “stop support for M23 and immediately leave the DRC without pre -preparation.”
According to Professor Zhou, China’s statement is likely who provided strong evidence of Rwanda M23 support.
“This is the main consensus at the UN Security Council,” he added.
“The problem lasts long enough, and everyone knows that the main situation is in their hearts. No longer need to suffocate.”
Neither the Mission of China in the UN nor its Embassy in London replied that when asked why China criticized Ruanda.
But Important for China from the well -known Mineral Dr. Congo can be a factor.
The struggle for the Eastern Doctor of the Congo was concentrated in the provinces of the North Kiva and the Southern Kiva, where many Chinese gold mines live.
It is unclear how these mines influenced the fighting.
The M23 also seized an area containing a coltan ore, which China imports in large volumes.
The metal Tantalum used in cars and everyday electronics from TVs to mobile phones is extracted from this ore, and Dr. Congo is a source of 40% of the world food.
In December 2024, the UN Expert Group stated that M23 smuggled Colton’s Rwan of Dr. Congo. He also noted that the exports of Colton Rwanda from 2022 to 2023 increased by 50%.
Although Rwanda has their Coltan mines in Rwanda, analysts say they can take into account such a large increase in production.
It is not yet clear whether the volume or price of the colton, which was imported by China, has suffered.
Another mineral that China imports from Dr. Congo is Cobalt, which is crucial for the lithium battery.
However, Chinese cobalt mining operations are primarily in the southern D -Congo, away from the conflict zones in the east.
Dozens of Chinese companies, many of which are state -owned, are also building roads, telecommunications and hydropower at Dr. Congo. But it seems that the impact on these actions is still minimal.
China supplies weapons to both Rwanda and Dr. Congo.
Over the past two decades, Rwanda’s military has been bought by Chinese armored vehicles, artillery and anti -tank missiles, the International Peace Study (Sipri) analytical center reports.
China for the first time in 2024 placed a military attaché to the country.
While UN experts say Rwanda’s military has armed M23, it is unclear whether it uses a rebel group of Chinese weapons.
Congolese’s armed forces bought Chinese armored carriers and drones.
They also own Chinese tanks, which were purchased in 1976, but were still used recently in 2022.
It is reported that drones have at least used in the fight against M23.
The Rwanda Embassy in Beijing stated that ties with China remain “excellent and productive”, and Rwanda did not comment on China’s statement about the fights of the Eastern Doctor of Congo.
Chinese Ambassador to Dr. Congo, Zhao Bin, conducted a discussion with the President of the Congolese Senate in early February, but the details of the meeting were not announced.
China’s economic activity in both countries is very deep. They are part of the Chinese belts and roads aimed at pressing China closer to the world through investment and infrastructure projects.
In Rwanda, China has financed stadiums, schools and highways. Chinese loans are also financial infrastructure projects – a loan for financing the dam and the irrigation system, which estimated $ 40 million (£ 31 million) in January.
Over the years, most of the goods imported into Rwanda come from China.
When it comes to China’s economic ties with Dr. Congo, the UN database shows that China has been the main trading partner of Dr. Congo for many years.
China has gone a long length to ensure access to Dr. Congo’s mineral wealth.
According to Chinese loans in Africa in Africa, mainly to finance the road and the bridge, mainly to finance the road and the bridge, mainly for the financing of the road and the bridge, as well as the country’s electricity, as well as the country’s electricity, as well as electricity in Africa.
China has financed and built other large -scale infrastructure projects in Dr. Congo, including hydroelectric power plants and a dry port.
These investments may assume that China’s long -term interest is quickly finding a conflict solution.
 Getty Images/BBC
Getty Images/BBC