Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

The brain plays a big role in the aging processand scientists think they have pinpointed the specific cells that control it.
In a study of mice, researchers at the Allen Institute identified certain cells that show “big changes” with age, particularly in one particular “hot spot,” according to a news release.
The mice were chosen because their brains are “very similar”. human brains.
FRIENDS AND FAMILY CAN PROTECT AGAINST HEART HEART, STROKE AND TYPE 2 DIABETES, RESEARCH SUGGESTS
“Our brain is made up of thousands of cell types that have different functions,” Hongkui Zeng, co-author of the study and director of the Allen Institute for Brain Science in Seattle, told Fox News Digital. “Our study shows that different types of cells are differently susceptible to the aging process.”
The research, funded by the National Institutes of Health, was published in the journal Nature.
Scientists at the Allen Institute believe they have pinpointed the specific brain cells that control aging. (iStock)
The researchers used RNA sequencing and brain mapping tools to analyze more than 1.2 million brain cells from young mice (2 months) and old mice (18 months).
FIGHTING DEMENTIA MEANS READING, PRAYING AND LISTENING TO MUSIC MORE: STUDY
The researchers noted that 18-month-old mice are roughly equivalent to a “middle-aged human.”
The researchers grouped the cells into 847 different types and also identified almost 2500 genes which changed with aging, according to Zeng.
The researchers said the mice (not pictured) were chosen because their brains “have many similarities” to the human brain. (iStock)
Cells that have been linked to aging showed increased inflammation and a decline in “neuronal function.”
“Changes in these genes indicate impairment of neuronal structure and function in many types of neurons and glial cells, as well as increased immune response and inflammation in types of immune and vascular (blood vessel) brain cells,” detailed Zeng.
5 MAIN DISCOVERIES BY SCIENTISTS IN 2024.
The cells that underwent the greatest changes were in the hypothalamus, a part of the brain associated with food intake, energy balance and metabolism, the researchers noted.
This suggests that this area is an “aging hot spot,” Zeng noted, and that there may be a link between diet, lifestyle factorsbrain aging and the risk of age-related cognitive impairment.
“Aging is a critical risk factor for many brain diseases.”
“The results of the study confirm the opinion that the preservation of a healthy lifestylepromoting a healthy metabolic state and reducing inflammation in the body and brain can slow or delay the aging process and reduce the risk of age-related brain diseases,” he said.
The hope is that the discovery could lead to new age-related therapies to improve the function of these cells and help prevent neurodegenerative diseases, according to the researchers.
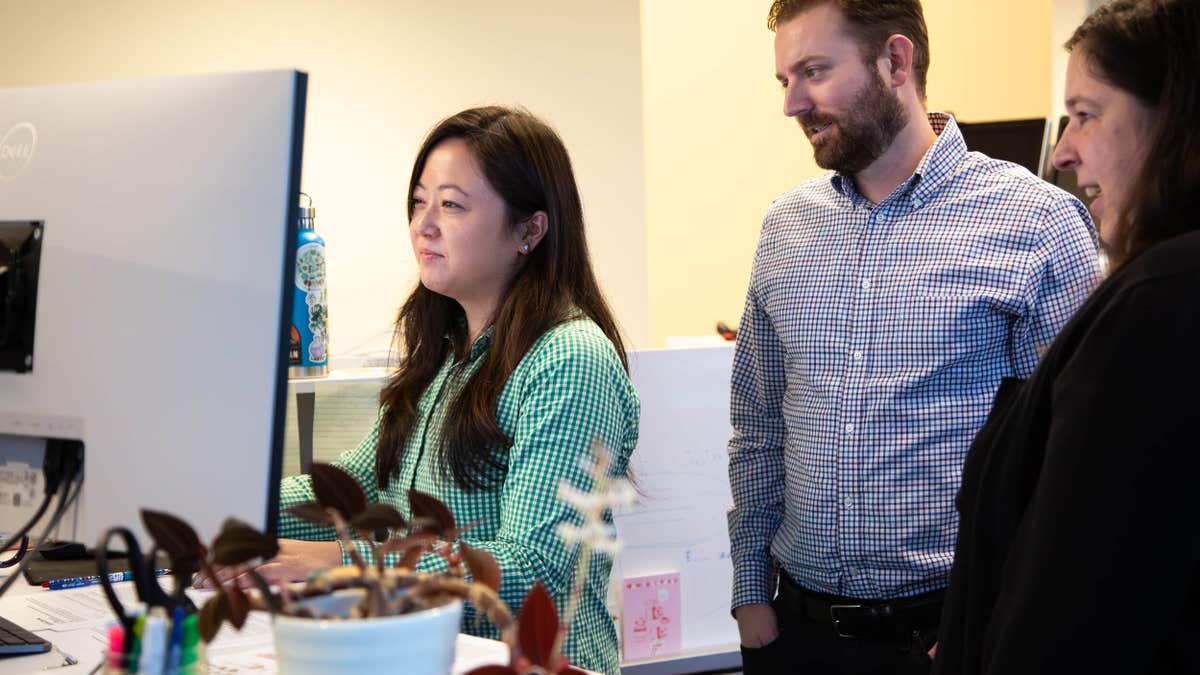

Researchers from the study discuss the results at the Allen Institute. (Allen Institute)
“Aging is the most important risk factor for many brain diseases,” Zeng noted.
“Our study provides a highly detailed genetic map of which brain cell types may be most affected by aging and suggests new genes and target cells for developing new treatments for aging-related brain diseases.”
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS PROGRAM
The study did have some limitations, the authors acknowledged.
“The main limitation of our study is that the results are correlational,” Zeng said.
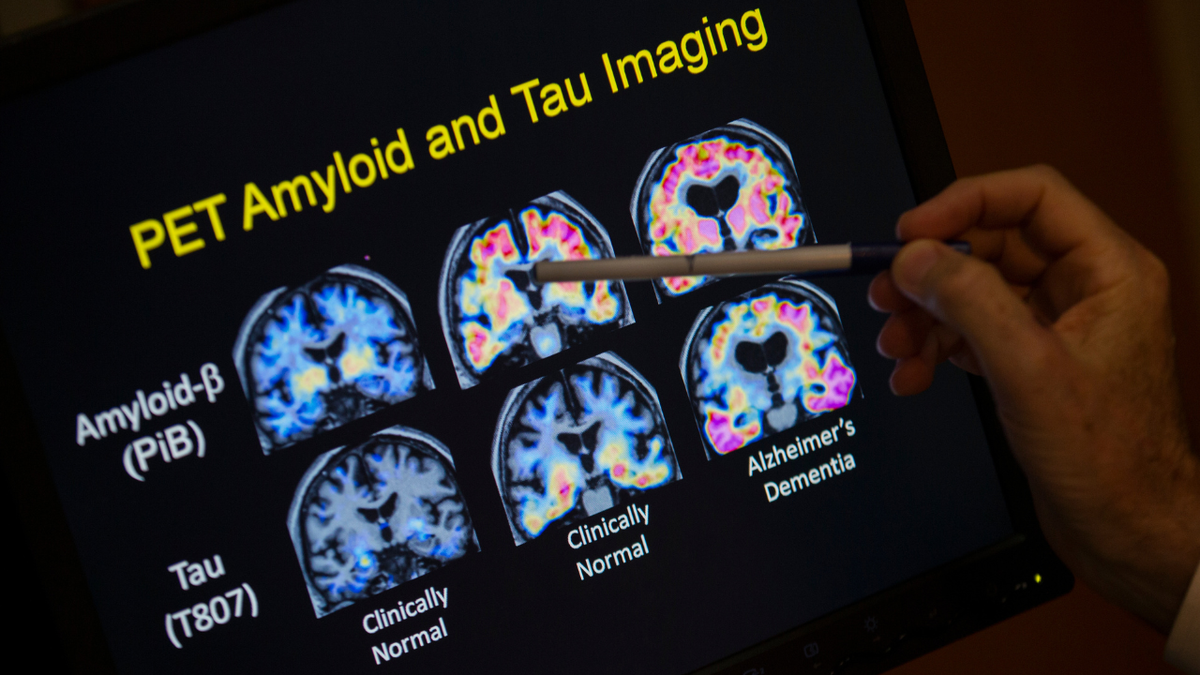
Inflammation plays a role in chronic age-related diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, the neuroscientist noted. (AP Photo/Evan Vucci, File)
“We do not yet know whether changes in gene expression seen in specific cell types are the cause of brain aging. Our study lays the groundwork by providing a detailed genetic map and target cells.”
Zeng urged future studies to investigate the role of cells in aging and determine whether reversing the changes could delay the aging process.
CLICK HERE TO SUBSCRIBE TO OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
Dr. Ernest Lee Murray, Fr licensed neurologist from Jackson-Madison County General Hospital in Jackson, Tennessee, commented that the new study adds to existing evidence supporting the role of diet in human brain health.
According to Murray, who was not involved in the study, the detailed “road map of the brain” will be very useful for future research on aging and possible treatments.
The detailed “road map of the brain” discovered during the study will be very useful for future research on aging and possible therapeutic agents, experts agree. (iStock)
It has been known for some time that inflammation plays a role in chronic age-related diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease– noted the neurologist.
“A growing body of evidence suggests that many chronic diseases are preventable, and it often comes down to diet and exercise” he told Fox News Digital.
For more health articles visit www.foxnews.com/health
“Changing your diet to eliminate processed foods and adopting certain habits, such as intermittent fasting, have been shown to reduce the cellular inflammation that appears to drive so many diseases.”